Vector Parametric Form
Vector Parametric Form - Web this video shows an example of how to write the solution set of a system of linear equations in parametric vector form. Web finding vector and parametric equations from the endpoints of the line segment. Web vector and parametric form. Multiplying a vector by a scalar. X1 = 1 + 2λ , x2 = 3 + 4λ , x3 = 5 + 6λ , x 1 = 1 + 2 λ , x 2 = 3 + 4 λ , x 3 = 5 + 6 λ , then the parametric vector form would be. Web the parametric form. However, in those cases the graph may no longer be a curve in space. This called a parameterized equation for the same line. The vector that the function gives can be a vector in whatever dimension we need it to be. Note as well that a vector function can be a function of two or more variables.
Web vector and parametric form. Web the parametric form. Web finding vector and parametric equations from the endpoints of the line segment. Web a vector function is a function that takes one or more variables, one in this case, and returns a vector. (x, y, z) = (1 − 5z, − 1 − 2z, z) z any real number. Web what is a parametric vector form? Web finding the three types of equations of a line that passes through a particular point and is perpendicular to a vector equation. X1 = 1 + 2λ , x2 = 3 + 4λ , x3 = 5 + 6λ , x 1 = 1 + 2 λ , x 2 = 3 + 4 λ , x 3 = 5 + 6 λ , then the parametric vector form would be. This is also the process of finding the basis of the null space. Web adding vectors algebraically & graphically.
Web the parametric form. Express in vector and parametric form, the line through these points. The componentsa,bandcofvare called thedirection numbersof the line. Found two points on the line: Web finding the three types of equations of a line that passes through a particular point and is perpendicular to a vector equation. Magnitude & direction to component. For instance, setting z = 0 in the last example gives the solution ( x , y , z )= ( 1, − 1,0 ) , and setting z = 1 gives the solution ( x , y , z )= ( − 4, − 3,1 ). 1 hr 39 min 9 examples. Web but probably it means something like this: Web finding vector and parametric equations from the endpoints of the line segment.
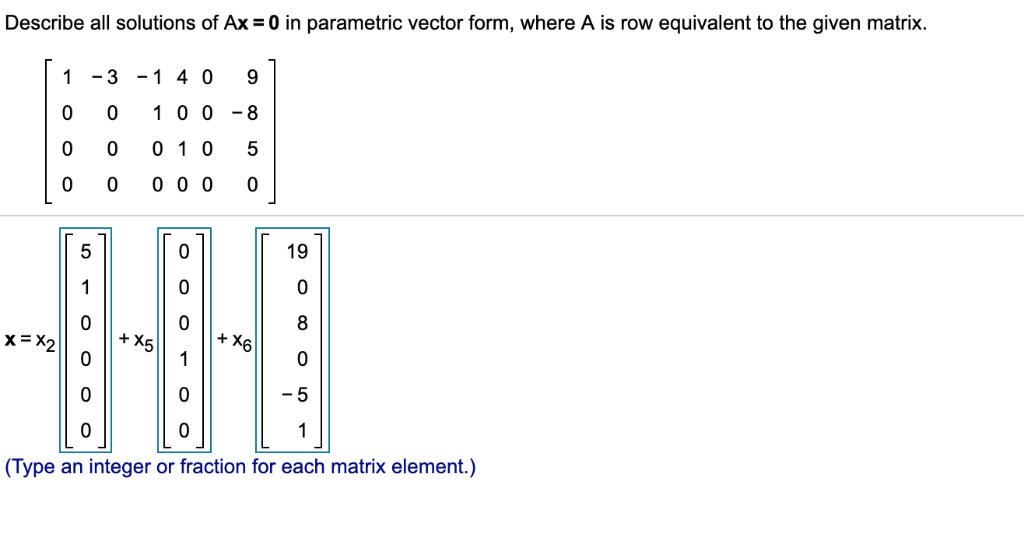
Solved Describe all solutions of Ax=0 in parametric vector
For matrices there is no such thing as division, you can multiply but can’t divide. Web this video explains how to write the parametric vector form of a homogeneous system of equations, ax = 0. Transforming a vector into parametric form. X = ( 1 3 5) + λ ( 2 4 6). Web this video shows an example of.
Sec 1.5 Rec parametric vector form YouTube
I have found the cartesian equation, but cannot find the parametric vector form. Web a vector function is a function that takes one or more variables, one in this case, and returns a vector. Finding the concavity (second derivative) of a parametric curve. Web the one on the form $(x,y,z) = (x_0,y_0,z_0) + t (a,b,c)$. Web adding vectors algebraically &.
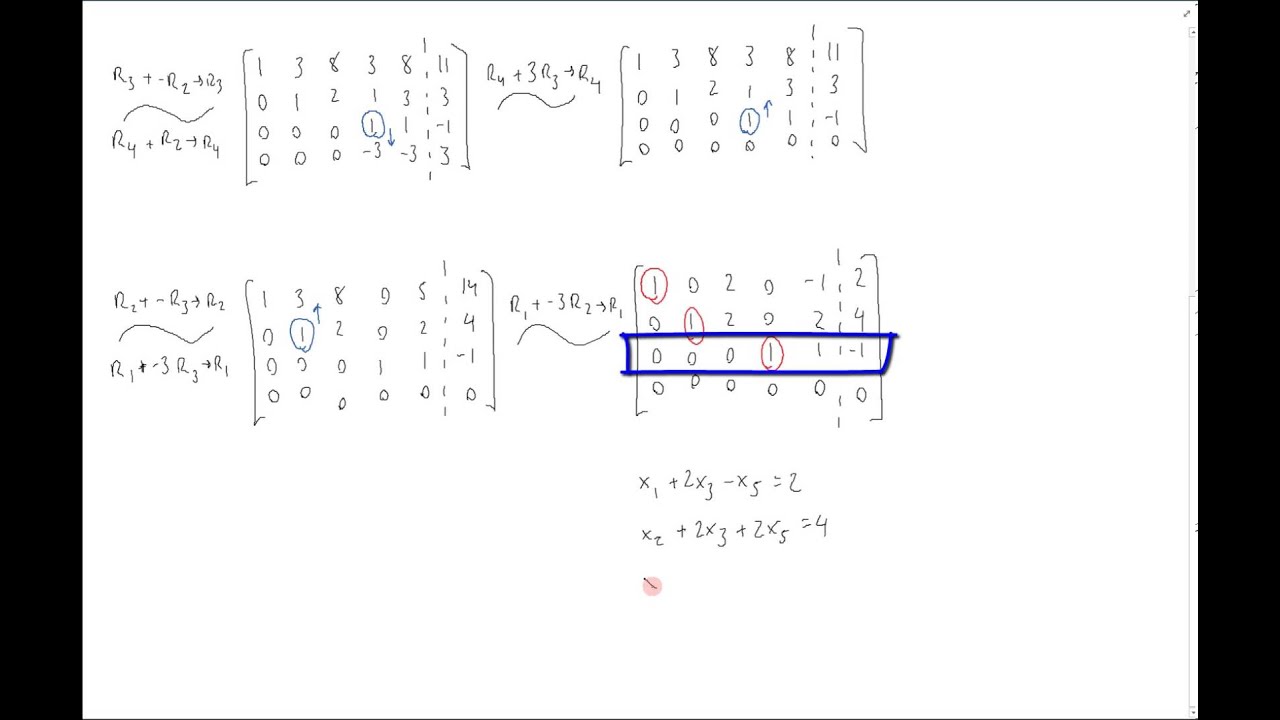
Solved Find the parametric vector form of the solution of
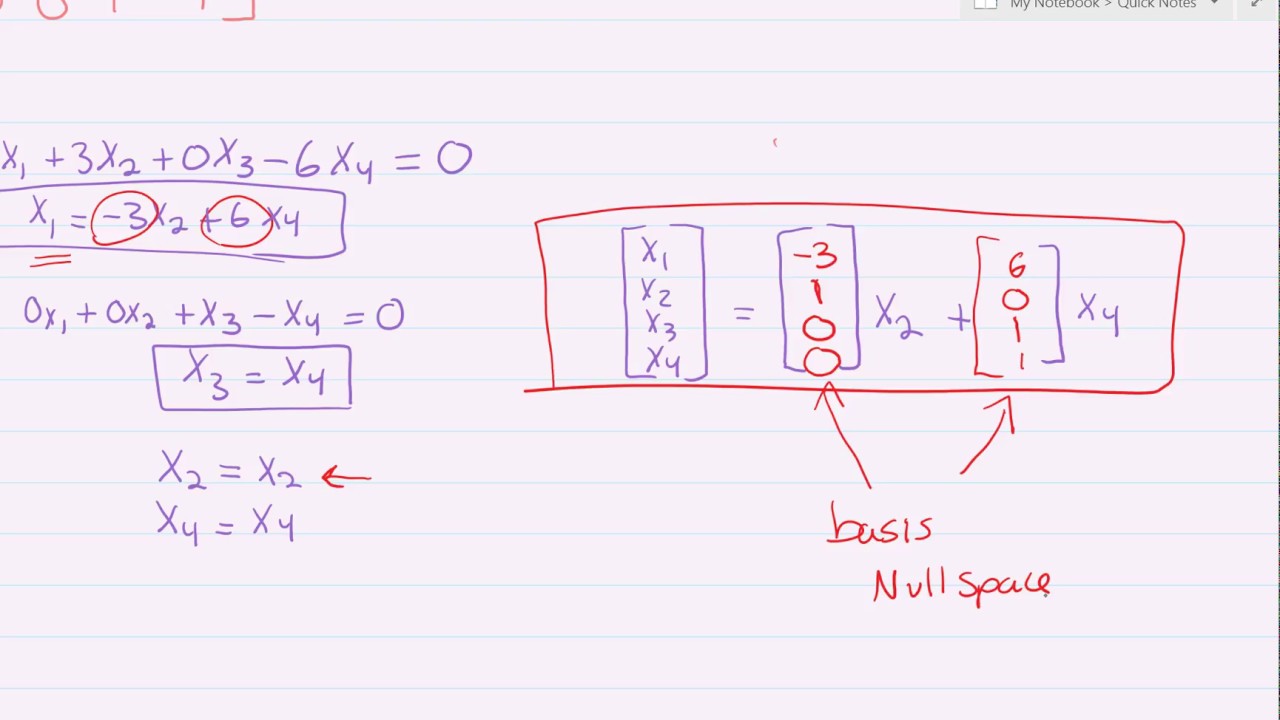
Wait a moment and try again. (x, y, z) = (1 − 5z, − 1 − 2z, z) z any real number. It is an expression that produces all points. Web given the parametric form for the solution to a linear system, we can obtain specific solutions by replacing the free variables with any specific real numbers. I have found.
202.3d Parametric Vector Form YouTube
Web finding the three types of equations of a line that passes through a particular point and is perpendicular to a vector equation. Web in mathematics, a parametric equation defines a group of quantities as functions of one or more independent variables called parameters. This called a parameterized equation for the same line. Web but probably it means something like.
4.2.3 Vector, Cartesian and Parametric Forms YouTube
Web adding vectors algebraically & graphically. Hence, the vector form of the equation of this line is ⃑ 𝑟 = ( 𝑥 , 𝑦 ) + 𝑡 ( 𝑎 , 𝑏 ). X1 = 1 + 2λ , x2 = 3 + 4λ , x3 = 5 + 6λ , x 1 = 1 + 2 λ , x 2.
Parametric Vector at Collection of Parametric Vector
Write the parametric and symmetric equations for Vector equation of a line suppose a line in contains the two different points and. (x, y, z) = (1 − 5z, − 1 − 2z, z) z any real number. {x = 1 − 5z y = − 1 − 2z. Web finding the three types of equations of a line that.
Example Parametric Vector Form of Solution YouTube
So what i did was the following in order: For matrices there is no such thing as division, you can multiply but can’t divide. Finding the slope of a parametric curve. Magnitude & direction to component. Express in vector and parametric form, the line through these points.
Parametric Vector Form and Free Variables [Passing Linear Algebra
Transforming a vector into parametric form. For matrices there is no such thing as division, you can multiply but can’t divide. Then the vector equation of the line containingr0and parallel tovis =h1;2;0i+th1; Web the one on the form $(x,y,z) = (x_0,y_0,z_0) + t (a,b,c)$. Where $(x_0,y_0,z_0)$ is the starting position (vector) and $(a,b,c)$ is a direction vector of the line.
Vector Parametric Form Flat Mathematics Stack Exchange
Found two points on the line: Hence, the vector form of the equation of this line is ⃑ 𝑟 = ( 𝑥 , 𝑦 ) + 𝑡 ( 𝑎 , 𝑏 ). Web finding vector and parametric equations from the endpoints of the line segment. Finding the concavity (second derivative) of a parametric curve. Finding the slope of a parametric.
Parametric vector form of solutions to a system of equations example
Then the vector equation of the line containingr0and parallel tovis =h1;2;0i+th1; Express in vector and parametric form, the line through these points. Can be written as follows: Web given the parametric form for the solution to a linear system, we can obtain specific solutions by replacing the free variables with any specific real numbers. The componentsa,bandcofvare called thedirection numbersof the.
X1 = 1 + 2Λ , X2 = 3 + 4Λ , X3 = 5 + 6Λ , X 1 = 1 + 2 Λ , X 2 = 3 + 4 Λ , X 3 = 5 + 6 Λ , Then The Parametric Vector Form Would Be.
Then the vector equation of the line containingr0and parallel tovis =h1;2;0i+th1; So what i did was the following in order: Web by writing the vector equation of the line interms of components, we obtain theparametric equationsof the line, x=x0+at; Web adding vectors algebraically & graphically.
Given A → = ( − 3, 5, 3) And B → = ( 7, − 4, 2).
However, in those cases the graph may no longer be a curve in space. For instance, setting z = 0 in the last example gives the solution ( x , y , z )= ( 1, − 1,0 ) , and setting z = 1 gives the solution ( x , y , z )= ( − 4, − 3,1 ). Express in vector and parametric form, the line through these points. Found two points on the line:
Let And Be The Position Vectors Of These Two Points, Respectively.
Wait a moment and try again. This called a parameterized equation for the same line. Web given the parametric form for the solution to a linear system, we can obtain specific solutions by replacing the free variables with any specific real numbers. Web the one on the form $(x,y,z) = (x_0,y_0,z_0) + t (a,b,c)$.
Calculating Area Enclosed By A Parametric Function.
For matrices there is no such thing as division, you can multiply but can’t divide. Web the parametric form. Finding the concavity (second derivative) of a parametric curve. Here is my working out: