How Many Covalent Bonds Can Each Carbon Atom Form
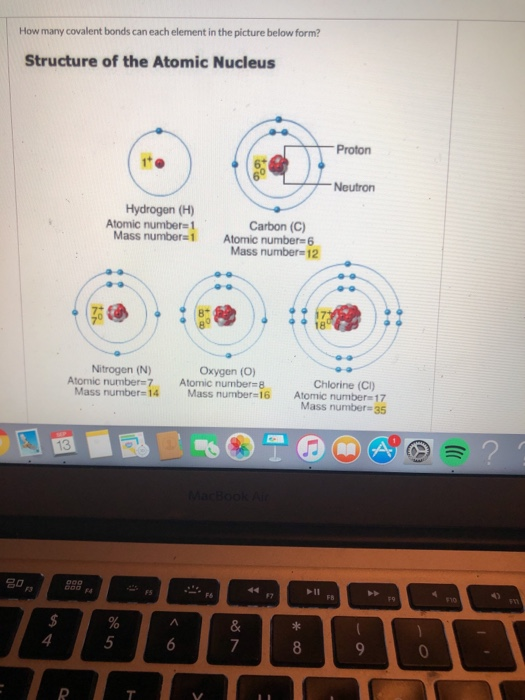
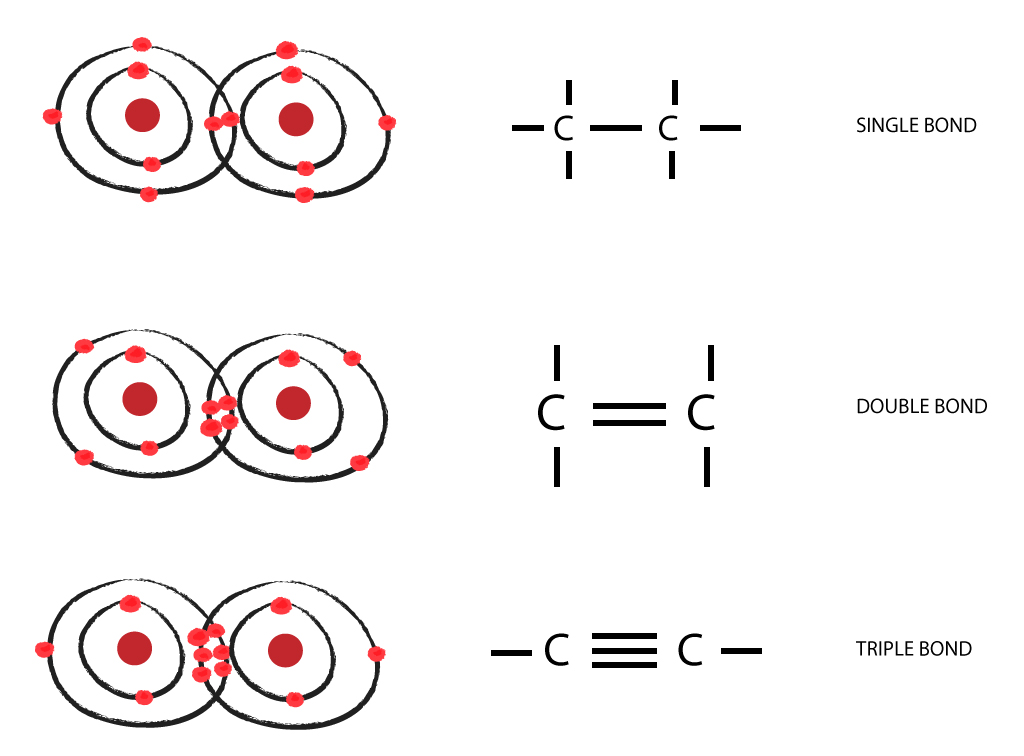
How Many Covalent Bonds Can Each Carbon Atom Form - And group 7a form one bond. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane (ch 4),. Web a double bond is formed when two atoms use two electron pairs to form two covalent bonds; A triple bond results when two atoms share three electron pairs to form three covalent. This means that it has six protons and six electrons. Covalent bonds are bonds that are formed between nonmetals. Group 6a form 2 bonds; Web carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Web carbon can form four covalent bonds. The atomic number of carbon is 6.
Web 4 rows typically, the atoms of group 4a form 4 covalent bonds; This means that it has six protons and six electrons. Group 5a form 3 bonds; Web a double bond is formed when two atoms use two electron pairs to form two covalent bonds; The most common form is the single bond : With hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and other heteroatoms. Web carbon has four valence electrons, so it can achieve a full outer energy level by forming four covalent bonds. Group 6a form 2 bonds; Web a molecule can have multiple single bonds. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane (ch 4),.
And group 7a form one bond. Carbon atoms can join together to make molecules. Web because carbon has four electrons in its valence (outer) shell, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. The number of electrons required to obtain. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. Web typically, the atoms of group 4a form 4 covalent bonds; When it bonds only with hydrogen, it forms compounds called. For example, water, h 2 o, has two single bonds, one between each hydrogen atom and the oxygen atom (fig. Group 6a form 2 bonds; This enables carbon to share four.
Carbon — Role and Importance to Life Expii
Web a double bond is formed when two atoms use two electron pairs to form two covalent bonds; The atomic number of carbon is 6. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane (ch 4),. Group 5a form 3 bonds; Web two atoms of the same element can be joined together in covalent molecules.
We ‘Share’ the Oil field with others in Europe, having a claim to the
This means that it has six protons and six electrons. The most common form is the single bond : Web because carbon has four electrons in its valence (outer) shell, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. The atomic number of carbon is 6. Web each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds.
How Many Single Bonds Can Carbon Form fredhughesdesign
Web a double bond is formed when two atoms use two electron pairs to form two covalent bonds; Web the carbon atom has unique properties that allow it to form covalent bonds to as many as four different atoms, making this versatile element ideal to serve as the basic structural. Carbon has an unusual ability to bond to itself. Form.
Solved How many covalent bonds can each element in the
Group 5a form 3 bonds; Web 4 rows typically, the atoms of group 4a form 4 covalent bonds; Web two atoms of the same element can be joined together in covalent molecules. Carbon has an unusual ability to bond to itself. Web typically, the atoms of group 4a form 4 covalent bonds;
Carbon to Carbon Single, Double & Triple Bonds Surfguppy
Group 5a form 3 bonds; Group 5a form 3 bonds; Group 6a form 2 bonds; Web two atoms of the same element can be joined together in covalent molecules. Web the carbon atom has unique properties that allow it to form covalent bonds to as many as four different atoms, making this versatile element ideal to serve as the basic.
Covalent Bonding (Biology) — Definition & Role Expii
The most common form is the single bond : Web a double bond is formed when two atoms use two electron pairs to form two covalent bonds; Group 5a form 3 bonds; Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. Web the carbon atom has unique properties that allow it to form covalent bonds to as.
Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules The Building Blocks · Biology
Group 5a form 3 bonds; Web a molecule can have multiple single bonds. Web carbon has four valence electrons, so it can achieve a full outer energy level by forming four covalent bonds. When it bonds only with hydrogen, it forms compounds called. This enables carbon to share four.
2.2 Chemical Bonds Anatomy & Physiology
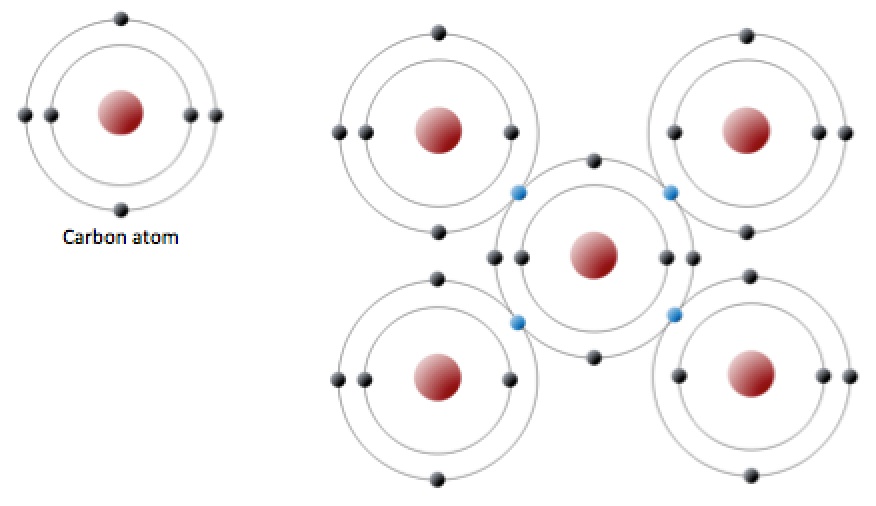
For example, water, h 2 o, has two single bonds, one between each hydrogen atom and the oxygen atom (fig. Web well, carbon can form up to four covalent bonds. When it bonds only with hydrogen, it forms compounds called. Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing a pair of electrons between itself.
2.2 Bonding and Lattices Physical Geology
Web carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Carbon has an unusual ability to bond to itself. In a covalent bond, two molecules share a couple of electrons. When it bonds only with hydrogen, it forms compounds called. Covalent bonds are bonds that are formed between nonmetals.
Bonding A Level Notes
Web carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing a pair of electrons between itself and each hydrogen (h) atom. Web a molecule can have multiple single bonds. Web a double bond is formed when two atoms use two electron pairs to form two covalent bonds;.
Covalent Bonds Are Bonds That Are Formed Between Nonmetals.
A bond composed of two electrons , one from each of the two. Web carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Carbon atoms can join together to make molecules. Form long c −c chains,.
For Example, Water, H 2 O, Has Two Single Bonds, One Between Each Hydrogen Atom And The Oxygen Atom (Fig.
The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane (ch 4),. Web each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds. When it bonds only with hydrogen, it forms compounds called. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules.
The Atomic Number Of Carbon Is 6.
Web carbon has four valence electrons, so it can achieve a full outer energy level by forming four covalent bonds. The bonds may be single, double, or triple. Web the carbon atom has unique properties that allow it to form covalent bonds to as many as four different atoms, making this versatile element ideal to serve as the basic structural. Web carbon can form four covalent bonds.
The Most Common Form Is The Single Bond :
Carbon has an unusual ability to bond to itself. Web because carbon has four electrons in its valence (outer) shell, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. Web a double bond is formed when two atoms use two electron pairs to form two covalent bonds; Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing a pair of electrons between itself and each hydrogen (h) atom.

.PNG)