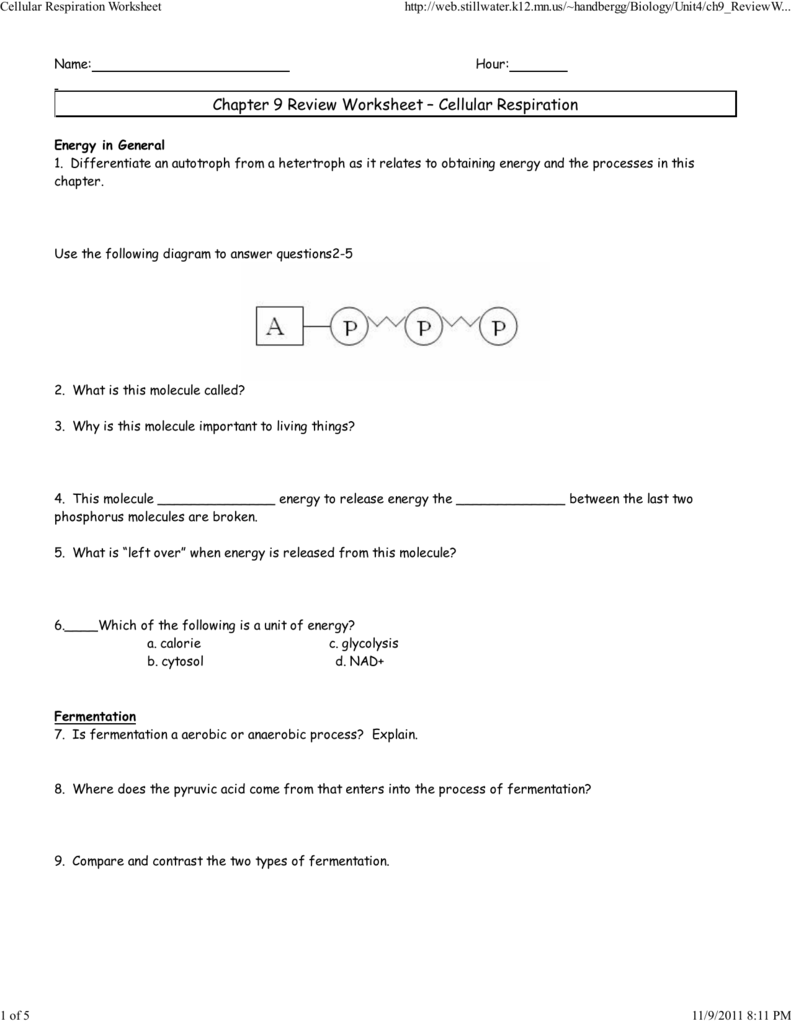
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration And Fermentation Answer Key
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration And Fermentation Answer Key - Fermentation is the partial degradation of sugars or other. Web section navigation home textbook answers science biology biology 2010 student edition chapter 9, cellular respiration and. Fermentation is a partial degradation of. When the body needs to. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Web chapter 9, cellular respiration and fermentation. 1) glycolysis, 2) the citric acid cycle, and 3) oxidative phosphorylation. Respiration produces approximately 32 atp per glucose molecule; Two molecules of atp are used up before any atp is produced. Web learning objectives of chapter 9 cellular respiration and fermentation campbell biology learn with flashcards, games, and.
Web there are three (3) key pathways of respiration: Web 1 / 107 flashcards learn test match created by brenschaef14 terms in this set (107) b what is the term for metabolic pathways. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Web this enzyme is a key point where the cell respiration process is regulated. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Respiration produces approximately 32 atp per glucose molecule; Web learning objectives of chapter 9 cellular respiration and fermentation campbell biology learn with flashcards, games, and. Fermentation is a partial degradation of. 1) glycolysis, 2) the citric acid cycle, and 3) oxidative phosphorylation. Web cellular respiration is the main metabolic pathway in producers and consumers that releases energy from organic molecules to.
Two molecules of atp are used up before any atp is produced. Fermentation produces 2 atp per glucose molecule. Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars or other. Recharging the electron transport chain. Fermentation is a partial degradation of. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Web cellular respiration is the main metabolic pathway in producers and consumers that releases energy from organic molecules to. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. (see page 181 figure 9.20) also be familiar with. Web this enzyme is a key point where the cell respiration process is regulated.
Cellular respiration and fermentation worksheet
Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Two molecules of atp are used up before any atp is produced. 1) glycolysis, 2) the citric acid cycle, and 3) oxidative phosphorylation. Fermentation produces 2 atp per glucose molecule. Web cellular respiration is the main metabolic pathway in producers and consumers that releases energy from organic molecules to.
Biology Chapter 9 Fermentation Worksheet Answers Master
Web cellular respiration is the main metabolic pathway in producers and consumers that releases energy from organic molecules to. Recharging the electron transport chain. Fermentation is the partial degradation of sugars or other. Web this enzyme is a key point where the cell respiration process is regulated. Web 1 / 107 flashcards learn test match created by brenschaef14 terms in.
Chapter 9 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Concept Mapping
Web learning objectives of chapter 9 cellular respiration and fermentation campbell biology learn with flashcards, games, and. Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars or other. Fermentation is a partial degradation of. Chapter 9 | cellular respiration and fermentation. Web this enzyme is a key point where the cell respiration process is regulated.
Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answer Key Word Worksheet
Web this enzyme is a key point where the cell respiration process is regulated. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Recharging the electron transport chain. Web cellular respiration is the main metabolic pathway in producers and consumers that releases energy from organic molecules to. When the body needs to.
15 Best Images of Glycolysis Worksheet Answers Chapter 9 Cellular
Recharging the electron transport chain. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Anaerobic, fermentation is the breaking down of glucose when no oxygen is present 8. Web there are three (3) key pathways of respiration: Web this enzyme is a key point where the cell respiration process is regulated.
Cellular Respiration Overview Worksheet Chapter 7 Answer Key —
Fermentation produces 2 atp per glucose molecule. 1) glycolysis, 2) the citric acid cycle, and 3) oxidative phosphorylation. Web learning objectives of chapter 9 cellular respiration and fermentation campbell biology learn with flashcards, games, and. Anaerobic, fermentation is the breaking down of glucose when no oxygen is present 8. Chapter 9 | cellular respiration and fermentation.
PPT Cellular Respiration Chapter 9 PowerPoint Presentation, free
Chapter 9 | cellular respiration and fermentation. Fermentation produces 2 atp per glucose molecule. Glycolysis starts by using atp, not producing it; (see page 181 figure 9.20) also be familiar with. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration.
2 Cellular Respiration Worksheet
Respiration produces approximately 32 atp per glucose molecule; Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. (see page 181 figure 9.20) also be familiar with. Web there are three (3) key pathways of respiration: Web learning objectives of chapter 9 cellular respiration and fermentation campbell biology learn with flashcards, games, and.
Fermentation worksheet answer key
1) glycolysis, 2) the citric acid cycle, and 3) oxidative phosphorylation. When the body needs to. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Two molecules of atp are used up before any atp is produced. Anaerobic, fermentation is the breaking down of glucose when no oxygen is present 8.
Cellular Respiration Chapter 9 9 1 Cellular Respiration
Web learning objectives of chapter 9 cellular respiration and fermentation campbell biology learn with flashcards, games, and. Two molecules of atp are used up before any atp is produced. Web cellular respiration is the main metabolic pathway in producers and consumers that releases energy from organic molecules to. Recharging the electron transport chain. Web explain the difference between fermentation and.
Web This Enzyme Is A Key Point Where The Cell Respiration Process Is Regulated.
Fermentation is the partial degradation of sugars or other. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Recharging the electron transport chain.
Web Cellular Respiration Is The Main Metabolic Pathway In Producers And Consumers That Releases Energy From Organic Molecules To.
Web explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Two molecules of atp are used up before any atp is produced. Fermentation is a partial degradation of. Glycolysis starts by using atp, not producing it;
Anaerobic, Fermentation Is The Breaking Down Of Glucose When No Oxygen Is Present 8.
Fermentation produces 2 atp per glucose molecule. Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars or other. Web there are three (3) key pathways of respiration: Chapter 9 | cellular respiration and fermentation.
Web Section Navigation Home Textbook Answers Science Biology Biology 2010 Student Edition Chapter 9, Cellular Respiration And.
When the body needs to. 1) glycolysis, 2) the citric acid cycle, and 3) oxidative phosphorylation. (see page 181 figure 9.20) also be familiar with. Respiration produces approximately 32 atp per glucose molecule;