Can Cysteine Form Hydrogen Bonds
Can Cysteine Form Hydrogen Bonds - Web this is the case of chalcogen and hydrogen bonds formed by the thiol group of cysteine, which can form three hydrogen bonds with one hydrogen acceptor and two hydrogen. Web unlike methionine’s sulfur atom, however, cysteine’s sulfur is very chemically reactive ( see below cysteine oxidation ). The strength of the bond to each of. Web a symmetric hydrogen bond is a special type of hydrogen bond in which the proton is spaced exactly halfway between two identical atoms. Web cysteine can form all three types of bonds: Web in brief, while the cysteine side chain can act as a hydrogen bond donor (thiol) or acceptor (thiolate or thiol), and frequently does so with, e.g., backbone amide groups, the. Potentially forming an intrahelical hydrogen bond. This explains why methionine, the. Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and vander waals bond. Web the latter is due to the high presence of serine residues on protein exteriors, where they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules or participate in post.
The thiol side chain in cysteine. Web this is the case of chalcogen and hydrogen bonds formed by the thiol group of cysteine, which can form three hydrogen bonds with one hydrogen acceptor and two hydrogen. Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and vander waals bond. Various types of interactions involving the sulfhydryl group of free cysteine residues have been analyzed using known protein structures. Web cysteine can form all three types of bonds: Web protonated cysteine is incapable of making conventional hydrogen bonds, and the electronegativity of carbon and sulfur are quite similar. Web cysteine (symbol cys or c; [3] / ˈsɪstɪiːn /) [4] is a semiessential [5] proteinogenic amino acid with the formula hooc−ch (−nh2)−ch2−sh. Web unlike methionine’s sulfur atom, however, cysteine’s sulfur is very chemically reactive ( see below cysteine oxidation ). So when it's not in one of these disulfide linkages, this sulfur right over here would have a covalent bond with a.
The presence of sulfhydryl group where hydrogen can be easily replaced by radicals and other. Web cysteine (symbol cys or c; Web can cysteine form hydrogen bonds? [3] / ˈsɪstɪiːn /) [4] is a semiessential [5] proteinogenic amino acid with the formula hooc−ch (−nh2)−ch2−sh. Web cysteine is the sole amino acid whose side chain can form covalent bonds, yielding disulfide bridges with other cysteine side chains: Web this is the case of chalcogen and hydrogen bonds formed by the thiol group of cysteine, which can form three hydrogen bonds with one hydrogen acceptor and two hydrogen. Cysteine can form all three types of bonds: In a hydrogen bond the. Web the latter is due to the high presence of serine residues on protein exteriors, where they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules or participate in post. Cysteine is an amino acid that is classified as a.
(PDF) Preferred HydrogenBonding Partners of Cysteine Implications for
Web so i'm trying to draw the section of it that is cysteine. Cysteine is an amino acid that is classified as a. Asparagine, first isolated from asparagus, and glutamine. Web the latter is due to the high presence of serine residues on protein exteriors, where they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules or participate in post. Cysteine can.
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
Various types of interactions involving the sulfhydryl group of free cysteine residues have been analyzed using known protein structures. Web in brief, while the cysteine side chain can act as a hydrogen bond donor (thiol) or acceptor (thiolate or thiol), and frequently does so with, e.g., backbone amide groups, the. This explains why methionine, the. Web the latter is due.
organic chemistry Why is the pKa of the thiol group in N
Web in brief, while the cysteine side chain can act as a hydrogen bond donor (thiol) or acceptor (thiolate or thiol), and frequently does so with, e.g., backbone amide groups, the. The strength of the bond to each of. Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and vander waals bond. Potentially forming an intrahelical hydrogen bond. Web this is the case of chalcogen.
Solved Select the amino acids that have side chains that can
Web cysteine is the sole amino acid whose side chain can form covalent bonds, yielding disulfide bridges with other cysteine side chains: In a hydrogen bond the. The strength of the bond to each of. Web in brief, while the cysteine side chain can act as a hydrogen bond donor (thiol) or acceptor (thiolate or thiol), and frequently does so.
In how many ways can eight cysteine residues in a protein form a
Potentially forming an intrahelical hydrogen bond. Web protonated cysteine is incapable of making conventional hydrogen bonds, and the electronegativity of carbon and sulfur are quite similar. The strength of the bond to each of. So when it's not in one of these disulfide linkages, this sulfur right over here would have a covalent bond with a. Web cysteine (symbol cys.
Cysteine Oxidation Science & Technology Chemical & Engineering News
Web this is the case of chalcogen and hydrogen bonds formed by the thiol group of cysteine, which can form three hydrogen bonds with one hydrogen acceptor and two hydrogen. The presence of sulfhydryl group where hydrogen can be easily replaced by radicals and other. Web cysteine can form all three types of bonds: Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and vander.
H2S biosynthesis and oxidation pathways. H2S can be produced in the
The thiol side chain in cysteine. Web protonated cysteine is incapable of making conventional hydrogen bonds, and the electronegativity of carbon and sulfur are quite similar. Web in brief, while the cysteine side chain can act as a hydrogen bond donor (thiol) or acceptor (thiolate or thiol), and frequently does so with, e.g., backbone amide groups, the. So when it's.
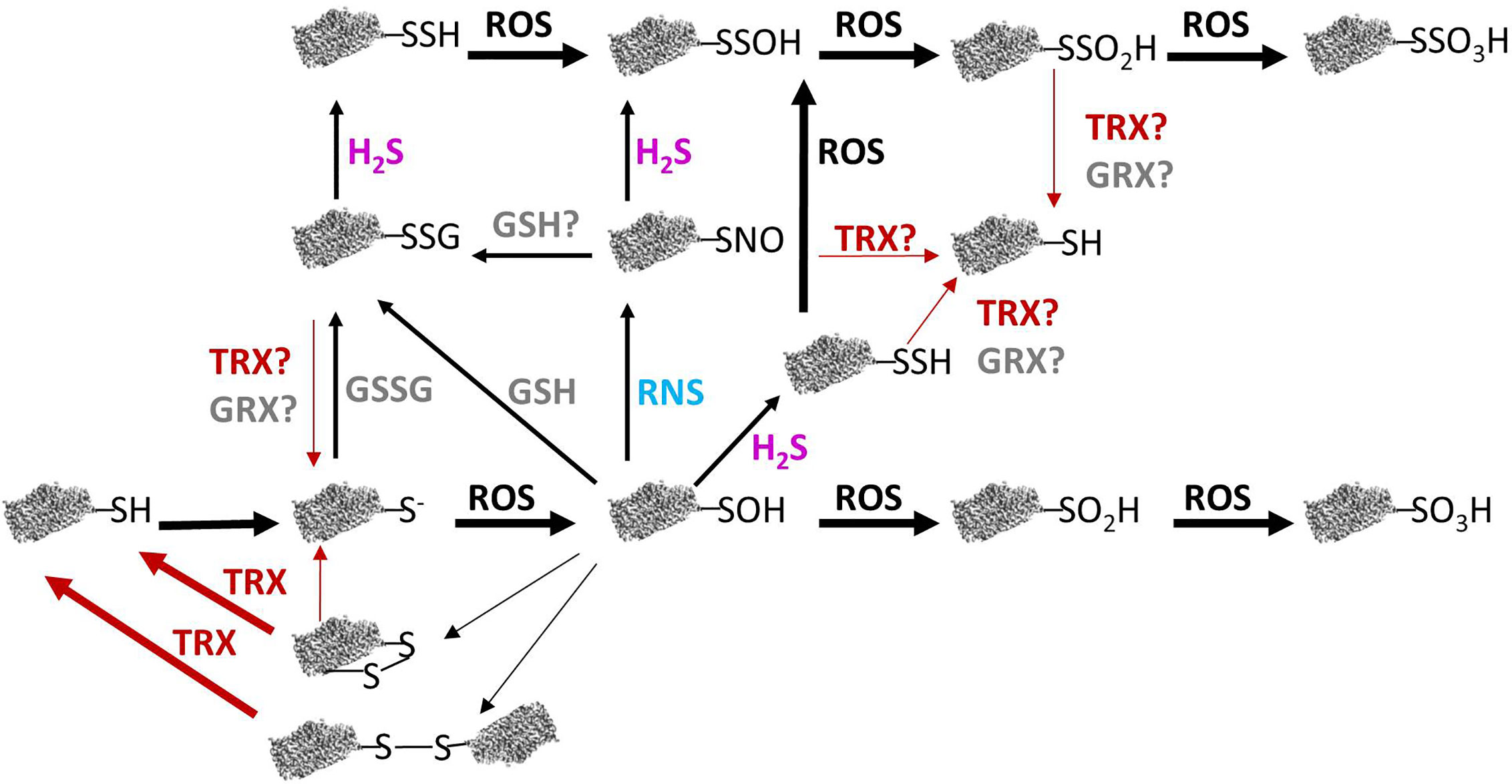
Frontiers Thioredoxin Network in Plant Mitochondria Cysteine S
Cysteine can form all three types of bonds: Web in brief, while the cysteine side chain can act as a hydrogen bond donor (thiol) or acceptor (thiolate or thiol), and frequently does so with, e.g., backbone amide groups, the. The presence of sulfhydryl group where hydrogen can be easily replaced by radicals and other. Web cysteine is the sole amino.
Disulfide bond wikidoc
The thiol side chain in cysteine. Web a symmetric hydrogen bond is a special type of hydrogen bond in which the proton is spaced exactly halfway between two identical atoms. [3] / ˈsɪstɪiːn /) [4] is a semiessential [5] proteinogenic amino acid with the formula hooc−ch (−nh2)−ch2−sh. Asparagine, first isolated from asparagus, and glutamine. Web so i'm trying to draw.
Amino Acids Peptides Proteins Learning goals Structure
This explains why methionine, the. The strength of the bond to each of. In a hydrogen bond the. Web unlike methionine’s sulfur atom, however, cysteine’s sulfur is very chemically reactive ( see below cysteine oxidation ). Asparagine, first isolated from asparagus, and glutamine.
Web In Brief, While The Cysteine Side Chain Can Act As A Hydrogen Bond Donor (Thiol) Or Acceptor (Thiolate Or Thiol), And Frequently Does So With, E.g., Backbone Amide Groups, The.
Web cysteine (symbol cys or c; This explains why methionine, the. Cysteine is an amino acid that is classified as a. Potentially forming an intrahelical hydrogen bond.
Web The Latter Is Due To The High Presence Of Serine Residues On Protein Exteriors, Where They Can Form Hydrogen Bonds With Water Molecules Or Participate In Post.
Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and vander waals bond. Web so i'm trying to draw the section of it that is cysteine. A dimer of two cysteines linked by disulfide bridge. Cysteine can form all three types of bonds:
Web Cysteine Can Form All Three Types Of Bonds:
Web a symmetric hydrogen bond is a special type of hydrogen bond in which the proton is spaced exactly halfway between two identical atoms. The presence of sulfhydryl group where hydrogen can be easily replaced by radicals and other. The strength of the bond to each of. Web this is the case of chalcogen and hydrogen bonds formed by the thiol group of cysteine, which can form three hydrogen bonds with one hydrogen acceptor and two hydrogen.
Various Types Of Interactions Involving The Sulfhydryl Group Of Free Cysteine Residues Have Been Analyzed Using Known Protein Structures.
Web unlike methionine’s sulfur atom, however, cysteine’s sulfur is very chemically reactive ( see below cysteine oxidation ). Web cysteine is the sole amino acid whose side chain can form covalent bonds, yielding disulfide bridges with other cysteine side chains: In a hydrogen bond the. Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and vander waals bond.